Intermediate Software Engineering
A Definition of Software Engineering
"The establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to obtain economically software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines"
(Pressman. 1992).
Structure Charts
Example:
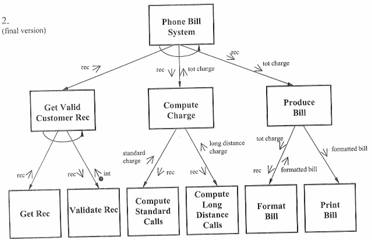
The structured Chart is a diagram which shows the interaction between each function (or module) within a program sequence. The above example shows the interactions of each function which make up the phone bill system.
The Symbols:
| This image symbolizes a function (or process). | |
 |
This image symbolizes a loop |
 |
This image symbolizes the passing of data between functions |
 |
This image symbolizes the passing of a new variable that a function has set. |
 |
this image symbolizes that one of the following options must be true. |
 |
This image symbolizes that one or none of the following options are true. |
Nassi Schneiderman Diagrams
The Nassi Schneiderman Diagram is a way to visually represent a program in a low level design. The structure is ease for a programmer to read and understand.
Key Facts
- Developed in 1973 by Nassi and Schneiderman
- The diagram represents the tasks which are contained within each function of a program.
- We start creating the diagram by first drawing a rectangle that represents the whole function.
- Each rectangle within the main rectangle symbolizes each process or task within the function.
Example:

Software Design Principles
The following software design principles are always followed when designing and building an Object-Oriented system:
- Modularity
- Information Hiding
- Coupling and Cohesion
However, the principles above can also be applied to other methods of programming.
Coupling and Cohesion
Coupling is the degree of connectedness between classes. Coupling increases when a class becomes more interdependent.
Different types of Coupling:
- Normal Coupling
- Data Coupling
- Stamp Coupling
- Control Coupling
- Comman Coupling
- Content Coupling
Cohesion implies that a component or class encapsulates only attributes and operations that are closely related to one another and to the calss or component itself (Pressman 2004).
Different Types of Cohesion:
- Functional Cohesion
- Sequential Cohesion
- Communicational Cohesion
- Procedural Cohesion
- Temporal Cohesion
- Logical Cohesion
- Coincidental Cohesion
Object-Oriented system: Objects and Classes
Objects
An object is an entity that has a state. An object has a collection of attributes and operations that are used to define and manipulate the object. Essentially, an object is an instance of a class.
Classes
A class is a conceptual description of a set of objects. An example of a class would be CARS, an instance of the class CARS would be FORD. FORD will therefore be an object of the class CARS.

UML Sequence Diagram
Example:
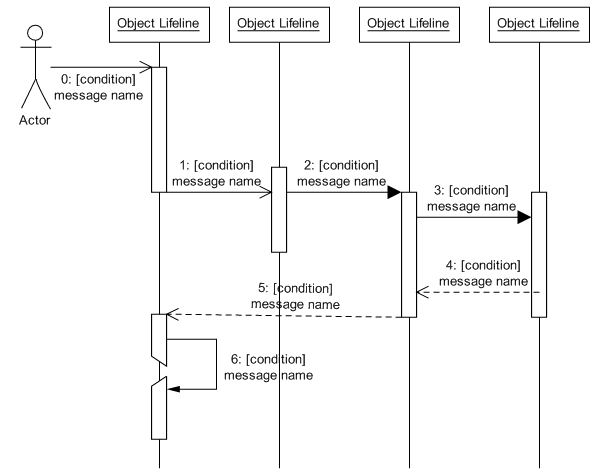
"Sequence diagrams depict the dynamic behavior of elements that make up a system as they interact over time" (Si Alhir, 2003).
CRC Diagrams (Class Responsibility Collaboration)
Example:

Responsibilities
The Class Responsibility Collaboration diagram is a way to diagrammatically Show the interaction between classes.
Collaborators
If an operation within a class needs to interact with a second class then the class name of the second class is written in the collaboration column alongside that operation.
Class Relationships
There are many link types you can have in an object-oriented system and they are:
- Inheritance - This is where the sub-class gains all the attributes and operations from the super class that it is connected to. An example of an inheritance relationship is a super class called person and its sub-class called doctor. In this example, the doctor is a person so the doctor class will gain the same attributes as the person class. The sub class however, may have extra attributes and operations apart from the one inherited.
- Aggregation - This is where the sub class is a part of the super class. An example of an aggregation relationship is a super class called car and a sub-class called wheels. In this example, the wheels are a part of the car but it does not inherit any of the cars attributes or operations.
- Association - This relationship is no as clear-cut as the inheritance and aggregation relationships. An example of an association relationship is a super class called department and the sub-class called employee. The relationship name in this example is that the department employs (or has) employees.
- Instantiation - This relationship is not like any other. Insantiation is not a relationship between classes but the relationship between a class and an object.
- Meta Class - The meta class relationship is where a class that define classes.
Testing
Verification
Are we building the product right? Verification is the part of testing where we have to check whether the program meets the client specification; does the program do what the user asked for? This part of testing should occur throughout the software development cycle.
Validation
Are we building the right product? Validation is the part of testing where we have to check whether the program does what the user wants and needs.
Testing Stages
- Unit Testing
- Intergration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Alpha Testing
- Beta Testing
- Regression Testing
White Box Testing
Another name for white box testing is "Glass Box Testing" because the tester is able to see the source code wile testing it. Test cases are created from the analysis of the source code.
Black Box Testing
The tester does not create test cases based on the source code of the application but from the requirements specification. These tests are created to test whether the program is doing what it is supposed to do.
Z Formal Specification Language
A formal specification is simply a description of a system using a mathematical notation (Bowen. 2003).
Z Schema
| N | Natural Numbers |
| N1 | Natural Numbers Starting From 1 |
| P | Power Set |
| # | Cardinality |
| {} | Empty Set |
| ' | Prime (new) |
| U | Union |
| \ | Difference |
| V | OR |
| ^ | AND |
| ? | Input |
| ! | Output |
| Changed | |
| Unchanged | |
| Empty Set | |
| Is a Member of | |
| Is Not a member of | |
Universal Set |
|
Subset |
|
| <=> | Equivalence |
| => | Implies |
| | | Constraint |
| dom | Domain |
| ran | Range |
| y | Restriction |
□ |
Predicate |
¬ |
Not |
References
Bowen, Jonathan (2003). Formal Specification and Documentation using Z: A Case Study Approach. International Thomson Computer Press.
Si Alhir, Sinan (2003). Learning UML. United States of America: O'Reilly.
